Every 39 seconds, a WordPress website falls victim to a cyberattack. With over 43% of the internet running on WordPress, hackers have turned this popular platform into their primary target. The average cost of a single security breach globally is $4.45 million, yet most WordPress owners remain dangerously unprepared.

This comprehensive guide reveals exactly how to secure a WordPress site using proven strategies that protect against malware, brute force attacks, and data theft while maintaining optimal performance.
Table of Contents
- Essential WordPress Security Fundamentals
- Keep Your WordPress Core, Themes, and Plugins Updated
- Implement Strong Login Security and Authentication
- Essential Security Plugins and Tools
- Backup Solutions and Recovery Planning
- Advanced WordPress Security Hardening
- Choosing Secure Hosting and Infrastructure
- Monitoring and Incident Response
- Ongoing WordPress Security Maintenance
Essential WordPress Security Fundamentals
WordPress’s popularity makes it an attractive target for cybercriminals who can automate attacks against thousands of sites simultaneously. The platform’s extensive plugin ecosystem, while providing incredible functionality, also creates multiple potential entry points for malicious actors.
Common security vulnerabilities include outdated software, weak passwords, insecure plugins, and misconfigured server settings. According to WPScan, over 90% of reported WordPress vulnerabilities are caused by plugins, while weak authentication accounts for another significant portion of successful attacks. These statistics underscore the importance of comprehensive security measures, rather than relying solely on single solutions.
The Cost of Security Breaches
The financial impact of security breaches extends far beyond immediate cleanup costs. Businesses face potential revenue loss from downtime, damaged reputation, decreased search rankings, and possible legal consequences if customer data is compromised. Google blacklists approximately 10,000 websites daily for malware or phishing, demonstrating the search engine’s commitment to protecting users from compromised sites.
Risk Reduction Strategy
WordPress security operates on risk reduction principles rather than complete risk elimination. No system can guarantee 100% security, but implementing multiple layers of protection significantly reduces vulnerability. This defense-in-depth approach combines preventive measures, detection systems, and response procedures to create robust protection against evolving threats.
Modern attackers use sophisticated techniques, including SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), and distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks. They often target automated vulnerabilities, seeking sites with known weaknesses rather than manually targeting specific businesses. Understanding these attack patterns helps website owners implement appropriate countermeasures and prioritize security investments effectively.
Keep Your WordPress Core, Themes, and Plugins Updated
Regular wordpress updates form the foundation of effective WordPress security. WordPress core developers continuously identify and patch security vulnerabilities, releasing updates that address newly discovered threats. Delaying these updates leaves sites exposed to known exploits that attackers actively scan for across the internet.
WordPress core updates. WordPress introduced automatic updates for minor releases, but major updates still require manual initiation. Site owners should enable automatic updates for security patches while carefully managing major version upgrades. This approach ensures critical security fixes are applied immediately while allowing time to test compatibility with existing themes and plugins.
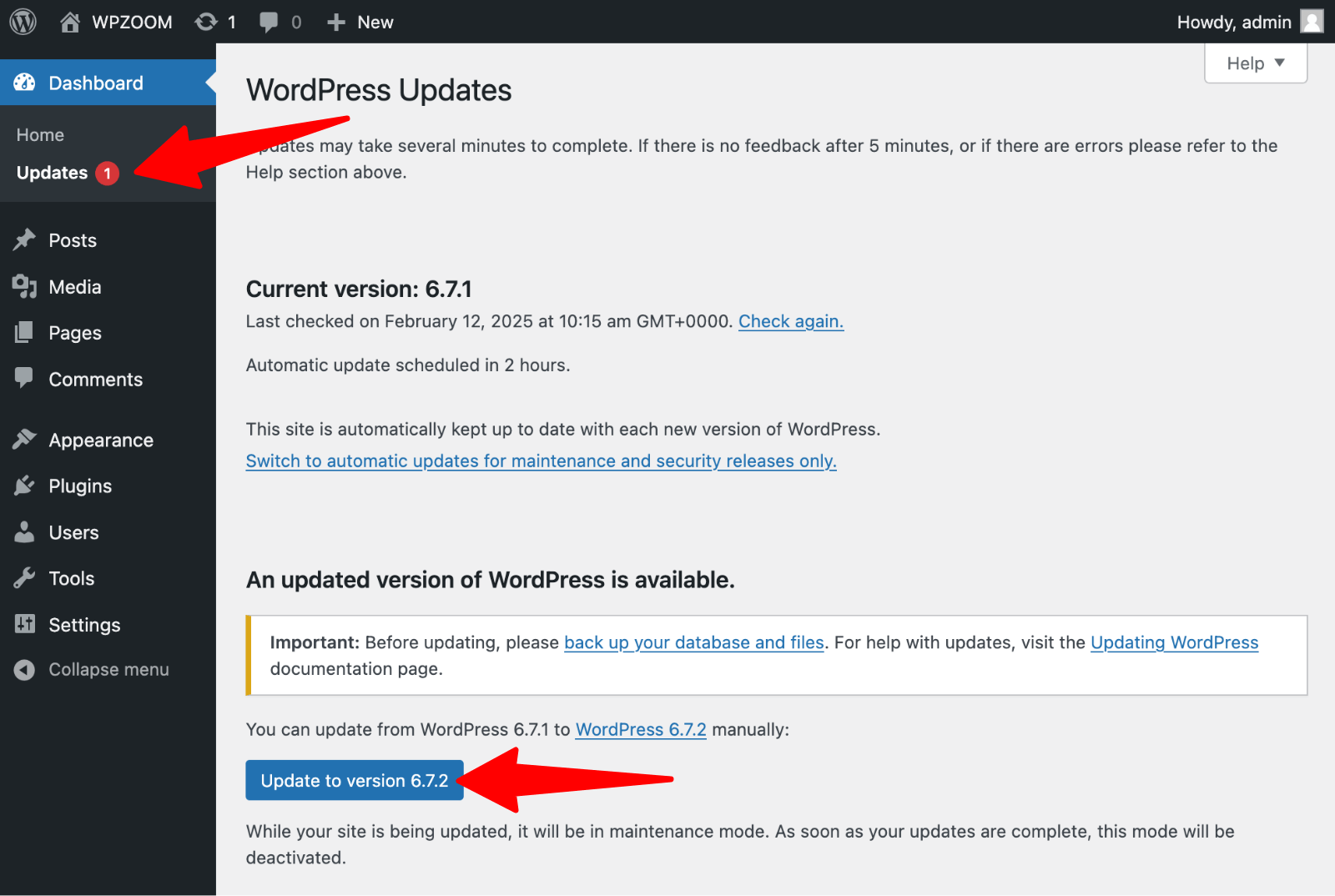
Plugin and theme updates deserve equal attention since these components often contain the most serious security vulnerabilities. Many site owners install plugins and themes, then forget about maintenance, creating long-term security risks. Establishing a regular update schedule, ideally on a weekly basis, helps maintain current security patches across all site components.
🚨 Important! Before updating, always create complete backups of your website files and database. Test updates on staging environments when possible, especially for major WordPress releases or significant plugin changes. This practice prevents update-related issues from affecting live sites while ensuring security patches are applied promptly.
Remove unused plugins and themes immediately rather than simply deactivating them. Inactive plugins still pose security risks, as their files remain accessible to attackers. Even deactivated plugins can be exploited if they contain vulnerabilities, making complete removal the safest approach for unused components.
Monitor the update frequencies and support responsiveness of plugin and theme developers. Plugins that haven’t been updated in several months may indicate abandoned projects with unpatched vulnerabilities. Replace outdated or unsupported plugins with actively maintained alternatives that offer similar functionality and provide ongoing security support.
Upgrade Your Website with a Premium WordPress Theme
Find a theme that you love and get a 10% discount at checkout with the FLASH10 code
Choose your theme
Implement Strong Login Security and Authentication
Login security represents the most critical defense against unauthorized access attempts. Strong, unique passwords combined with secure usernames create the first barrier against brute force attacks.
Avoid common usernames like “admin” or your business name, as these are frequently targeted in automated attacks.
Create passwords with these essential characteristics:
- At least 12 characters minimum
- Uppercase and lowercase letters
- Numbers and special characters
- No dictionary words or personal information
- Unique for each account
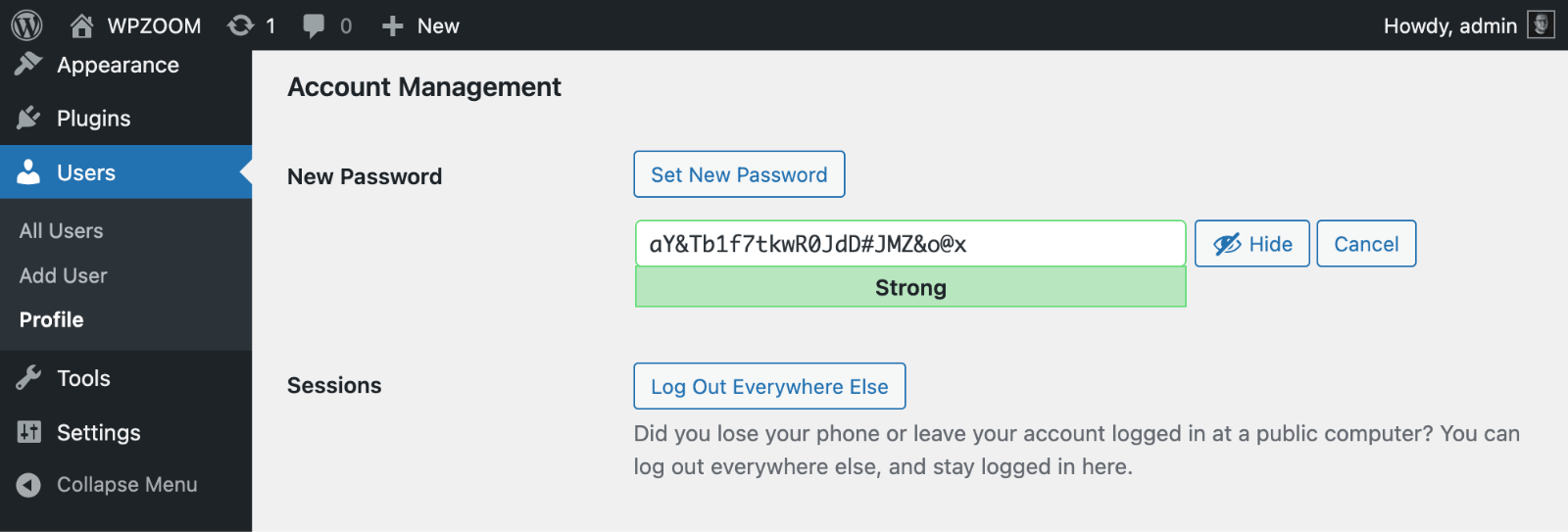
💡 Pro Tip. Use a password manager like Bitwarden to generate and store unique passwords for every account. This eliminates the dangerous practice of password reuse while making complex passwords manageable.
Two-factor authentication adds an essential second layer of protection beyond passwords. Even if attackers obtain login credentials, they cannot access accounts without the second authentication factor. Plugins like WP 2FA provide a straightforward two-factor authentication setup for WordPress sites.

Limiting login attempts prevents brute force attacks that try thousands of password combinations. Plugins such as Limit Login Attempts Reloaded automatically block IP addresses after a specified number of failed login attempts. Configure these plugins to allow reasonable retry attempts while blocking obvious attack patterns.
Consider changing your WordPress login URL from the default wp-admin endpoint. Plugins like WPS Hide Login move the login page to a custom URL, reducing automated attack attempts against standard WordPress locations. While this provides security through obscurity, it effectively reduces server load from constant attack attempts.
Implement proper user role management by assigning the minimal necessary permissions to each account. WordPress includes built-in roles from Administrator to Subscriber, each with specific capabilities. Regular audits of user accounts help identify unnecessary privileges and remove accounts for former employees or contractors who no longer require access.
Essential Security Plugins and Tools
Security plugins provide comprehensive protection through multiple security measures in single packages.
- Wordfence Security provides real-time threat detection, malware scanning, and firewall protection with both free and premium versions. The plugin’s threat intelligence feeds help identify emerging attack patterns and block malicious traffic automatically.
- All-In-One Security (AIOS) is perfectly described by its name. The plugin is a one-stop shop for most security needs. AIOS comes with a few exciting features in the free version and a relatively low cost for the premium version.
- Jetpack Protect offers a range of features and is a robust tool for protecting your site against various attacks and security threats. One of Jetpack‘s main selling points is that it was developed by the WordPress team.
Website firewall protection filters malicious traffic before it reaches your server. Cloud-based firewalls, such as Cloudflare or Sucuri’s WAF service, block attacks at the network level, reducing server load and preventing many common attack vectors. These services also offer content delivery network (CDN) benefits, enhancing site performance.
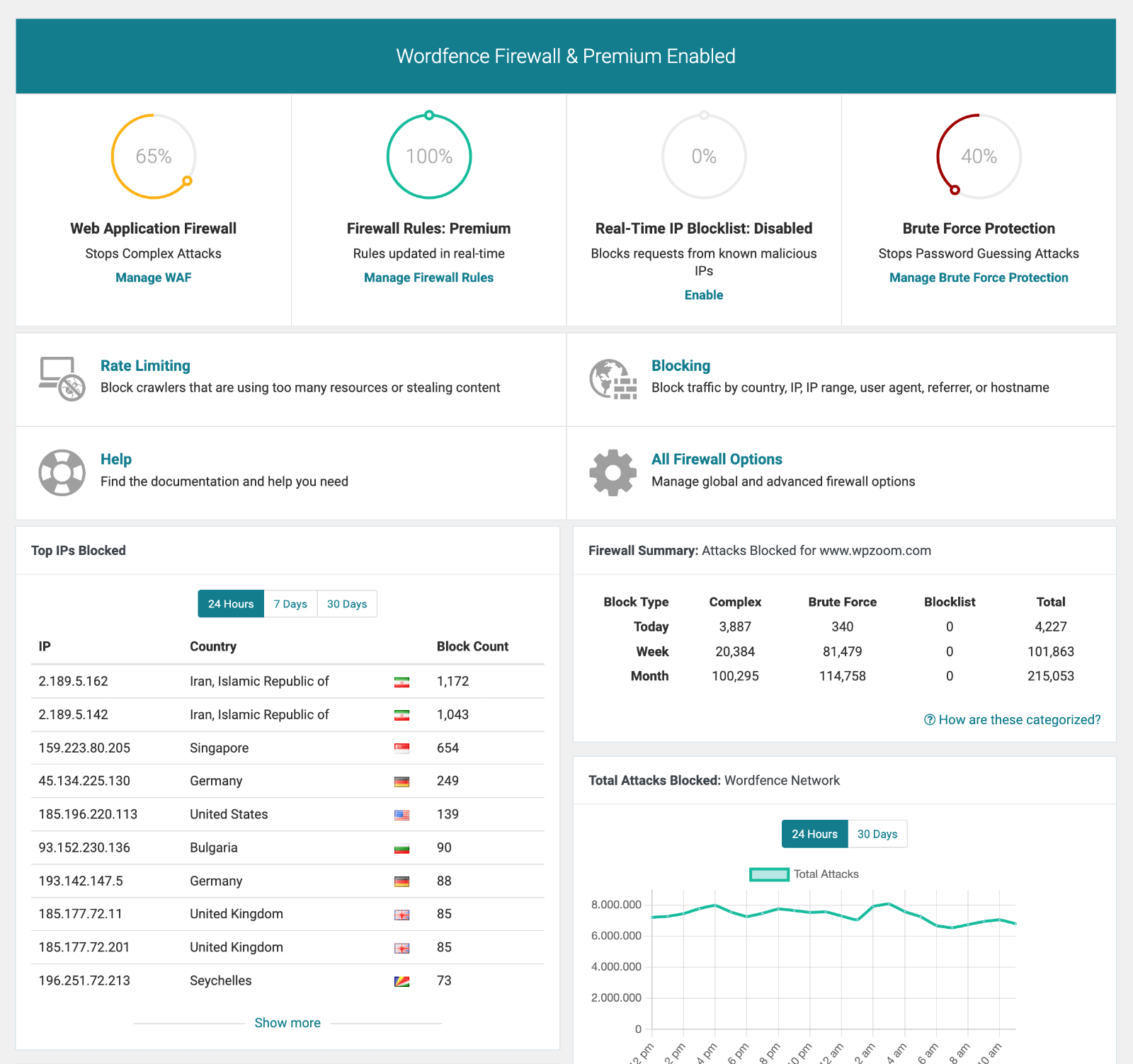
Malware scanning should occur regularly, not just after suspected infections. Automated scanners check for malicious code, suspicious file modifications, and known attack signatures. Configure scans to run daily or weekly, depending on site update frequency and risk tolerance.
Security monitoring and alerts keep site owners informed about potential threats and suspicious activities. Configure notifications for critical events, such as login attempts, file modifications, and plugin installations. Balance alert frequency with actionable information to avoid notification fatigue while maintaining security awareness.
Backup Solutions and Recovery Planning
Regular backup solutions provide essential insurance against security incidents, technical failures, and human errors. Comprehensive backups should include:
- All website files and custom modifications
- Complete MySQL database with all tables
- wp-content directory (themes, plugins, uploads)
- Configuration files (wp-config.php, .htaccess)
- Custom code and third-party integrations
Schedule automated backups at frequencies that match your content update patterns.
Store backups in off-site locations separate from your web server. Cloud storage services, such as Google Drive, Dropbox, or Amazon S3, provide secure and accessible backup storage that remains available even if your hosting server is compromised. Avoid storing backups on the same server as your website.
Test backup restoration procedures regularly to ensure backups are complete and functional. Many site owners discover backup problems only during emergencies when restoration becomes critical. Schedule quarterly restoration tests on staging environments to verify backup integrity and restoration processes.
Backup retention policies should strike a balance between storage costs and recovery needs. Maintain daily backups for recent changes, weekly backups for longer-term recovery, and monthly backups for historical reference. This tiered approach provides multiple recovery points while managing storage requirements efficiently.
Popular backup plugins, such as UpdraftPlus, Duplicator, or BlogVault, provide automated scheduling, cloud storage integration, and restoration capabilities. Select solutions that align with your technical expertise and recovery time requirements, while ensuring reliable and tested backup creation.
Advanced WordPress Security Hardening
SSL certificate installation encrypts data transmission between browsers and servers, protecting sensitive information from interception. Modern browsers display security warnings for non-HTTPS sites, which can affect user trust and search engine rankings. Most hosting providers offer free SSL certificates through Let’s Encrypt or include certificates in hosting packages.

File permission management controls access to critical WordPress files and directories. Set appropriate permissions for wp-config.php (600), .htaccess (644), and directory structures (755) to prevent unauthorized access while maintaining functionality. Incorrect permissions can either expose sensitive files or break site functionality.
Database security includes changing default table prefixes from “wp_” to custom values, reducing automated attack effectiveness. While not a complete security solution, custom prefixes make attacks slightly more difficult and demonstrate security awareness. Combine prefix changes with strong database passwords and restricted database user permissions.
Disable file editing within WordPress admin to prevent attackers from modifying theme and plugin files through the dashboard.
Add the following to wp-config.php to remove editing capabilities:
define('DISALLOW_FILE_EDIT', true);This forces legitimate changes through secure FTP access while blocking a common attack vector.
The .htaccess file enables server-level security configurations, including access restrictions, blocking PHP execution, and preventing directory browsing. Implement rules to protect wp-config.php, block access to sensitive directories, and prevent PHP execution in upload folders. Always back up .htaccess before modifications.
Hide WordPress version information to reduce targeted attacks against specific vulnerabilities. Remove version numbers from HTML headers, RSS feeds, and readme files that reveal installation details to attackers. While security through obscurity isn’t sufficient alone, it reduces automated scanning effectiveness.
Disable XML-RPC functionality unless specifically required for remote publishing or mobile applications. XML-RPC enables amplified brute force attacks and DDoS vectors that can overwhelm servers. Add XML-RPC blocking rules to your .htaccess file or use a security plugin to disable this functionality safely.
Choosing Secure Hosting and Infrastructure
Hosting providers play crucial roles in WordPress security through server-level protections, software maintenance, and incident response capabilities. Evaluate potential hosts based on these essential security features:
- Malware scanning and automated removal
- DDoS protection and traffic filtering
- Web application firewall (WAF) at the server level
- Regular security updates for server software
- SSL certificates included or easily available
- Daily automated backups with easy restoration
- 24/7 security monitoring and incident response
Managed WordPress hosting often provides superior security through specialized configurations, automatic updates, and expert support teams. These services typically include staging environments, automated backups, and security monitoring specifically designed for WordPress sites. While more expensive than shared hosting, managed services reduce security management overhead.
Server-level security considerations include PHP version management, database security, and isolation between customer accounts. Modern PHP versions include security improvements and performance optimizations that benefit WordPress sites. Ensure hosting providers maintain current software versions and provide upgrade paths for legacy installations.
Content delivery networks (CDNs) and firewall services provide additional security layers while improving site performance. Services like Cloudflare offer DDoS protection, bot filtering, and geographic content distribution that enhance both security and user experience. These services can block attacks before they reach origin servers.
Evaluate hosting support quality and security incident response procedures. Quality hosts provide 24/7 technical support with security expertise available during incidents. Review support response times, available communication channels, and escalation procedures for security-related issues.
Monitoring and Incident Response
Security monitoring provides early warning systems for potential threats and unauthorized activities. Implement monitoring for login attempts, file modifications, plugin installations, and changes to user accounts. Configure alerts for critical events while filtering routine activities to focus attention on genuine security concerns.
Activity logging creates audit trails for forensic analysis and compliance requirements. Log user actions, system changes, and security events with sufficient detail for investigation purposes. Plugins like WP Activity Log provide comprehensive logging capabilities with configurable retention periods and alert systems.
Recognize common signs of security breaches, including unexpected redirects, new user accounts, modified files, performance degradation, and search engine warnings. Early detection enables faster response and reduces potential damage from security incidents. Train team members to identify and report suspicious activities promptly.
Develop incident response procedures, including initial assessment, containment measures, investigation steps, and recovery processes. Document communication protocols, escalation procedures, and external resource contacts for complex incidents. Regular incident response exercises help teams respond effectively under pressure.
Blacklist monitoring alerts you when search engines or security services identify your site as potentially malicious. Services like Google Search Console, Sucuri SiteCheck, or VirusTotal provide monitoring and notification services for reputation management. A quick response to blacklisting helps minimize the impact on traffic and ranking.
Ongoing WordPress Security Maintenance
Establish regular security maintenance schedules, including update reviews, security scans, backup verification, and access audits. Weekly maintenance routines help identify issues before they become serious problems while ensuring security measures remain current and effective.
Conduct quarterly security audits reviewing user accounts, plugin inventory, access logs, and security configurations. Remove unnecessary accounts, update outdated plugins, and verify security settings remain appropriate for current needs. Document findings and implement improvements systematically.
Stay informed about WordPress security developments through official WordPress security announcements, plugin developer notifications, and security research publications. Subscribe to WordPress security mailing lists and follow reputable security researchers for timely threat intelligence.
Security training for team members ensures everyone understands their role in maintaining site security. Cover password management, phishing recognition, social engineering awareness, and incident reporting procedures. Regular training updates help teams stay current with evolving threats and security best practices.
Build security considerations into content management workflows, including image optimization, plugin evaluation, and user onboarding processes. Integrate security checks into regular website maintenance tasks rather than treating security as separate, occasional activities.
Document security policies and procedures for consistency and knowledge sharing. Include password requirements, update procedures, access management, and incident response protocols. Regular policy reviews ensure guidelines remain relevant and effective as threats evolve.
Ready to Build Your WordPress Site on a Secure Foundation?
WPZOOM’s premium WordPress themes are crafted with security best practices built in, featuring clean, optimized code that works seamlessly with top security plugins. Our themes receive regular updates and undergo thorough security testing, providing you with a solid foundation essential for comprehensive WordPress security.


